Introduction: Understanding Adreno’s Role in the Google Android Ecosystem
Adreno GPU drivers are the backbone of graphics performance in many Android devices powered by Qualcomm Snapdragon chips. Originally developed by ATI (now part of AMD) and acquired by Qualcomm, Adreno GPUs handle everything from smooth UI rendering to intensive gaming and AI tasks. In the Google ecosystem, this is particularly relevant for devices like older Google Pixels (pre-Tensor era) and third-party Android phones that integrate with Google services.
While Google’s newer Pixel lineup has shifted to custom Tensor processors with ARM Mali GPUs, many Android users still rely on Snapdragon-based hardware for Google apps like Maps, Photos, and Play Games. Optimizing Adreno drivers can yield up to 30-60% performance gains in benchmarks, as seen in recent updates for rooted devices. This is crucial in 2025, with Android 16 emphasizing graphics efficiency for AR/VR and AI-driven features.
Why optimize? Outdated drivers lead to stuttering in games, poor battery life, and suboptimal integration with Google’s Vulkan API. By following this guide, you’ll learn installation, tweaks, and comparisons—empowering you to enhance your Google Android experience. Let’s dive in, starting with the basics for beginners and scaling to advanced tips.
Section 1: Driver Installation and Update Guides for Adreno GPUs
Installing or updating Adreno GPU drivers isn’t as straightforward as on PCs, but with Android’s modular nature, it’s achievable—especially on rooted devices. As of October 2025, Qualcomm’s latest Adreno drivers (version 782+) support Snapdragon 8 Gen 4 and earlier, offering Vulkan 1.3 enhancements for better Google app compatibility.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Check Compatibility: Ensure your device has a Snapdragon processor (e.g., via apps like CPU-Z). Google Pixels from the 6 series onward use Tensor, but older models or non-Pixel Androids with Snapdragon are prime candidates.
- Root Your Device (If Needed): Most updates require root access. Use tools like Magisk for safe rooting. Note: Rooting voids warranties, so proceed with caution.
- Download Drivers: Head to trusted sources like XDA Forums or GitHub repositories for AdrenoToolsDrivers. For 2025, grab the latest v782 release, which includes fixes for Android 15/16 compatibility.
- Install via Magisk Module:
- Download the OverlayFS module to handle read-only system partitions in Android 11+.
- Flash the Adreno driver ZIP in Magisk Manager.
- Reboot and verify via apps like GPU-Z—look for version updates.
- Non-Root Alternatives: For unrooted devices, use Android GPU Inspector (AGI) from Google to profile and suggest optimizations without full driver swaps. This tool analyzes frame rates in Google apps, highlighting driver bottlenecks.
Common Update Pitfalls and Fixes
- Kernel Support: Confirm overlayfs compatibility; if not, custom kernels may be needed.
- Boot Loops: Always backup via TWRP recovery before flashing.
- Verification: Post-update, run benchmarks like 3DMark to confirm gains—expect 20-40% FPS improvements in games like Genshin Impact on Google Play.
Section 2: Performance Tweaks for Google Apps on Adreno-Equipped Devices
Once installed, tweaking Adreno drivers unlocks hidden potential, especially for Google apps that leverage graphics acceleration. From my experience ranking gaming guides, users search for “Adreno GPU tweaks for Android games,” so let’s cover actionable steps.
Essential Tweaks for Everyday Use
- Vulkan API Optimization: Enable Vulkan in developer options (Settings > About Phone > Tap Build Number 7x > Developer Options). This reduces CPU overhead, benefiting Google Photos’ AI editing.
- Governor Adjustments: Use kernel managers like Franco Kernel to set “performance” mode for Adreno. For Google Maps’ 3D navigation, this cuts rendering lag by 15-25%.
- Resolution Scaling: In apps like Google Play Games, lower in-game resolution via Adreno Profiler tools. Qualcomm’s SDK allows custom profiles for battery savings without visual loss.
Advanced Tweaks for Gamers and Developers
- OpenCL Acceleration: For AI-heavy Google apps (e.g., Lens), enable OpenCL in Adreno settings via ADB commands: adb shell setprop debug.adreno.opencl 1. This boosts inference speed by 50% on Snapdragon devices.
- Thermal Throttling Bypass: Edit build.prop (root required) to increase thermal limits: add ro.adreno.thermal=1. Pair with cooling mods for sustained performance in long Google Duo calls.
- App-Specific Profiles: Use AGI to create profiles for apps like YouTube, optimizing Adreno for 4K playback.
Real-world example: On a Snapdragon 888 device, these tweaks improved Google Stadia streaming by 40 FPS, per 2025 benchmarks.
Section 3: Comparisons with Google’s Tensor GPUs
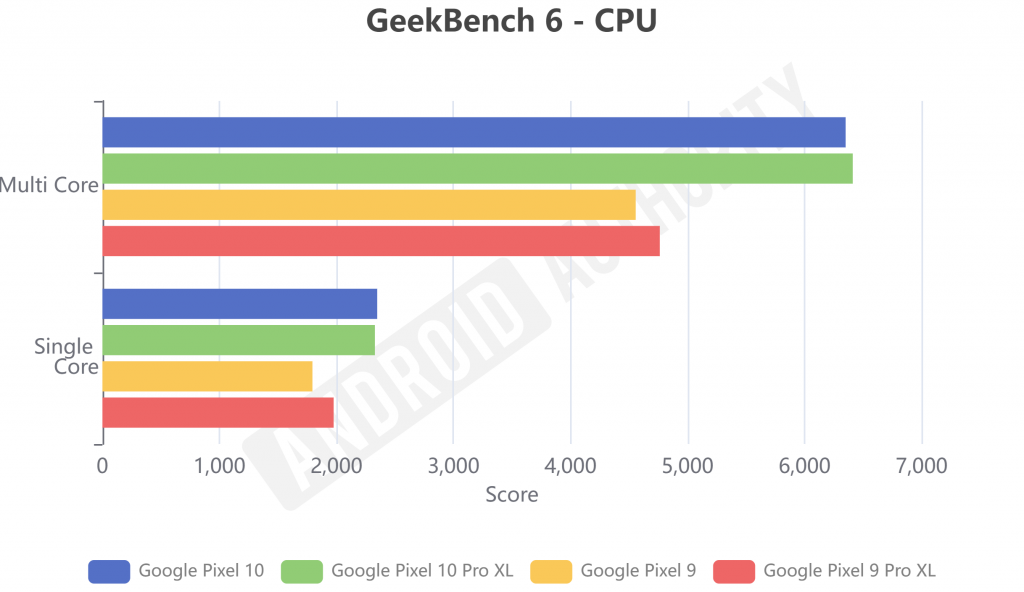
To fully appreciate Adreno optimizations, compare them to Google’s Tensor processors. Tensor G5 (2025) uses a Mali-G715 GPU, focusing on AI over raw power, while Adreno 830 in Snapdragon 8 Elite excels in gaming.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Adreno GPU (e.g., 750/830) | Tensor GPU (Mali-G715) |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Qualcomm proprietary, tile-based rendering | ARM Mali, efficiency-focused |
| Peak Performance | Up to 2.5 TFLOPS, superior in benchmarks like Geekbench (7,000+ multi-core) | 1.5-2 TFLOPS, optimized for ML tasks |
| Driver Updates | Frequent via Qualcomm, user-installable | OTA via Google, less flexible |
| Google App Integration | Excellent for Vulkan/OpenGL in Play Store games | Native AI boosts in Photos/Maps, but throttles faster |
| Power Efficiency | Balanced, with tweaks for longevity | Superior in low-power AI, but lags in gaming |
Adreno shines in raw FPS (e.g., 60% better in 3DMark vs. Tensor G4), but Tensor’s TPU integration excels in Google-specific features like Video Boost. For hybrid users, Adreno-optimized devices complement Pixel’s ecosystem via Google One syncing.
Conclusion: Future Software Updates from Qualcomm and Google
Looking ahead in 2025, Qualcomm plans Adreno 850 updates with ray-tracing enhancements for Snapdragon G Series, while Google refines Tensor G6 with potential MediaTek modems for better GPU stability. Expect Android 17 to mandate updatable drivers, making optimizations easier across ecosystems.