Phishing attacks surged in 2024, with enterprise users three times more likely to fall victim compared to the previous year, according to Netskope’s Cloud and Threat Report.
The study highlighted that 8.4 out of every 1,000 users clicked on phishing links each month, a sharp increase from 2.9 in 2023.
This surge reflects a significant shift in cybercriminal tactics, leveraging generative AI tools, search engine manipulation, and trusted platforms like Cloudflare to bypass traditional defenses.
“The main factors leading to this increase are cognitive fatigue (with users constantly being bombarded with phishing attempts) and the creativity and adaptability of the attackers in delivering harder-to-detect baits,” the company writes.
These evolving methods have outpaced traditional training programs aimed at teaching users to identify phishing attempts, exposing critical vulnerabilities in enterprise defenses.
The Role of Generative AI in Advanced Phishing Campaigns
The proliferation of generative AI tools has fundamentally changed the phishing landscape. Black-market platforms such as WormGPT and FraudGPT are widely used to craft phishing lures that are grammatically correct, localized, and tailored to specific industries.
These tools automate the creation of diverse, highly targeted messages, increasing the likelihood of success.
Related: AI-Driven Malware: How Fake Apps and CAPTCHAs Target Windows and macOS Users
“LLMs can provide better localization and more variety to try to evade spam filters and increase the probability of fooling the victim,” Ray Canzanese, director of Netskope Threat Labs, told CSO,” said Ray Canzanese, Director of Netskope Threat Labs.
Beyond text-based lures, attackers are deploying deepfake technologies to impersonate executives, making phishing attempts even more convincing. Deloitte’s survey revealed that 15% of executives reported incidents involving deepfake-enabled scams targeting financial systems in 2024.
Shifting Tactics: Search Engines and Trusted Platforms Take Center Stage
Phishing campaigns are no longer confined to email. Netskope’s data shows that search engines became a leading source of phishing clicks in 2024. Cybercriminals employed SEO poisoning and malicious advertising to ensure phishing pages ranked prominently in search results, exploiting user trust in search engines to drive traffic to fake login sites.
Additionally, attackers leveraged trusted platforms like Cloudflare Pages and Workers to scale phishing campaigns. A recent report by Fortra revealed a 198% increase in phishing incidents hosted on Cloudflare Pages and a 104% rise in attacks using Cloudflare Workers.
Related: Microsoft Teams Phishing Attacks Surge, Exploiting Fake IT Accounts and QR Codes
These platforms, designed for legitimate web development, inadvertently offer cybercriminals the scalability, security, and speed needed to execute convincing phishing operations.
“While an almost 200% increase in attacks being hosted on Cloudflare Pages is eye-opening on its own, the types of threats are what we really want to focus on. These platforms are not only being used to host convincing phishing sites, but also redirect to other malicious sites,” Zachary Travis, Threat Hunter II at Fortra, explained.
Using tools like Cloudflare Workers, attackers automate phishing campaigns and credential-stuffing operations, enhancing the effectiveness of their efforts.
Cloud Services Under Attack: Microsoft 365 and Adobe Among Top Targets
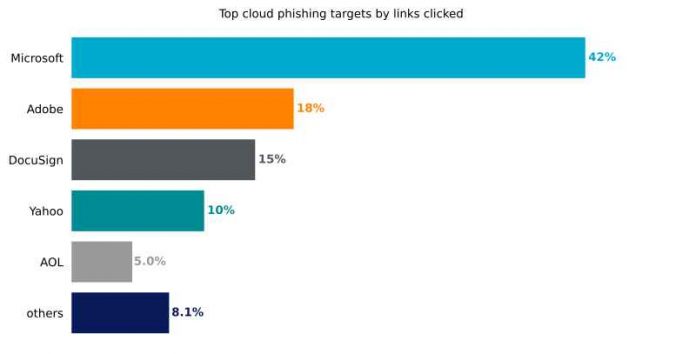
Cloud-based applications remain prime targets for phishing campaigns. According to Netskope, Microsoft 365 accounted for 42% of phishing attempts in 2024, followed by Adobe Document Cloud (18%) and DocuSign (15%). Phishing sites often mimic the login portals of these services to steal credentials, even offering options to log in through third-party providers like Yahoo or Outlook to increase their chances of success.
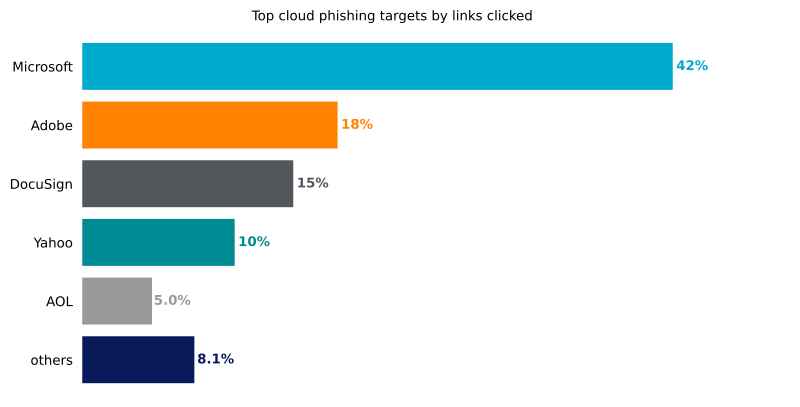

The popularity of Microsoft 365 as a target is unsurprising, given its widespread adoption in enterprises. Attackers aim to exploit these credentials for purposes ranging from business email compromise to data theft and further infiltration into organizational networks.
Related: Cybercriminals Use GitHub Fake Star Campaigns to Spread Scams and Malware
Technical Terms and Tactics Driving the Surge
Several advanced techniques and platforms are driving the success of phishing campaigns. For instance:
- SEO Poisoning: This involves manipulating search engine algorithms to rank malicious websites higher in search results, increasing the likelihood that users will click on them.
- Cloudflare Workers: A serverless computing platform that allows developers to run scripts closer to users for lower latency. Attackers exploit its functionality to automate phishing redirects, bypass traditional defenses, and scale operations.
- Malvertising: Cybercriminals use malicious ads to redirect users to phishing sites, leveraging legitimate ad networks to reach a broader audience.
These tactics illustrate the increasing sophistication of phishing campaigns, which now rely on exploiting user trust in technology rather than solely targeting individual ignorance.
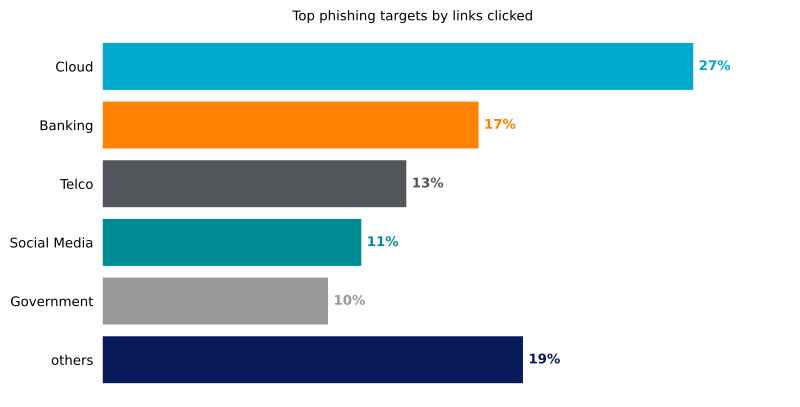

Cognitive Fatigue Weakens Defenses
Despite extensive user training, phishing click rates have risen sharply due to cognitive fatigue among employees. Workers face an overwhelming number of security decisions daily, such as evaluating the legitimacy of links or emails. This constant vigilance leads to decision fatigue, making even trained users susceptible to phishing attempts.
Netskope emphasized that attackers are adept at exploiting this vulnerability. By targeting non-email channels like search engines and cloud platforms, they reduce the efficacy of email-based phishing training and increase the probability of success.
Recommendations for Reducing Exposure to Phishing Risks
To combat the evolving phishing landscape, cybersecurity experts recommend a multi-faceted approach that combines advanced technology, policy enforcement, and user education. Organizations should:
- Inspect All Web Traffic: Monitoring HTTP and HTTPS traffic for phishing attempts, Trojans, and malware can prevent malicious content from reaching users.
- Restrict High-Risk Apps: Blocking access to unauthorized or high-risk generative AI tools can reduce vulnerabilities.
- Adopt Real-Time User Coaching: Providing employees with real-time guidance when interacting with potentially risky platforms or links can significantly lower phishing success rates.
- Leverage Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Deploying DLP tools to detect and block sensitive data sharing on unauthorized platforms helps protect organizational assets.
Real-time user coaching has proven especially effective, with Netskope reporting that users proceed with risky actions only 27% of the time when prompted with context-specific guidance.
The rapid evolution of phishing tactics underscores the necessity of adaptive security measures. Traditional training and static defenses are no longer sufficient in addressing the sophisticated strategies employed by cybercriminals. Advanced monitoring tools, behavioral analytics, and a proactive approach to cybersecurity policy are critical for mitigating risks in the modern enterprise environment.